EXECUTIVE SUMMARY AND POLICY ACTIONS
The recovery associated with the receding pandemic has slowed as a result of the Russian aggression in Ukraine. It has contributed to high inflation and is damaging the economic outlook, which led to increased financial market risks across the board. The economic and financial impact of the invasion has been felt globally, alongside enormous humanitarian consequences. Prices in energy and commodity markets have risen to record highs. Production and logistics costs have risen and household purchasing power has weakened. After a long period characterized by very low inflation and interest rates, policy rates are being raised in response to high inflation. The resulting higher financing costs and lower economic growth may put pressure on the government, and on corporate and household debt refinancing. It will likely also have negative impact on the credit quality of financial institution loan portfolios. Financial institutions are moreover faced with increased operational challenges associated with heightened cyber risks and the implementation of sanctions against Russia. The financial system has to date been resilient despite the increasing political and economic uncertainty.
In light of the above risks and uncertainties, the Joint Committee advises national competent authorities, financial institutions and market participants to take the following policy actions:
- Financial institutions and supervisors should continue to be prepared for a deterioration in asset quality in the financial sector. In light of persistent risks that have been amplified by the Russian invasion and a deteriorating macroeconomic outlook, combined with a build-up of medium-term risks with high uncertainty, supervisors should continue to closely monitor asset quality, including in real estate lending, in assets that have benefitted from previous support measures related to the pandemic, and in assets that are particularly vulnerable to rising inflation and to high energy- and commodity prices.
- The impact on financial institutions and market participants more broadly from further increases in policy rates and the potential for sudden increases in risk premia should be closely monitored. Inflationary pressures coupled with uncertainty on risk premia adjustment raise concerns over potential further market adjustments. Rising interest rates and yields are expected to improve the earnings outlook for banks given their interest rate sensitivity. They could also reduce the valuation of fixed income assets, and result in higher funding costs and operating costs, which might affect highly indebted borrowers’ abilities to service their loans. Credit risks related to the corporate and banking sector also remain a primary concern for insurers and for the credit quality of bond funds. High market volatility stemming from the above economic and geopolitical situation could also raise short-term concerns and disruptions for market infrastructures.
- Financial institutions and supervisors should be aware and closely monitor the impact of inflation risks. The economic consequences of the Russian aggression mainly channel through energy and commodity markets, trade restrictions due to sanctions and the possible fragmentation of the global economy. Financial fragmentation, including fragmentation of funding costs, could threaten financial stability and put pressure on price stability. Inflation is not only relevant from a risk perspective, but is expected to reflect also on the actual benefits and pensions, inflationary trends should be taken into account in the product testing, product monitoring and product review phases. Financial institutions and regulators should make extra efforts to ensure investor awareness on the effects of inflation on real returns of assets, and how these can vary across different types of assets.
- Supervisors should continue to monitor risks to retail investors some of whom buy assets, in particular crypto-assets and related products, without fully realizing the high risks involved. Some retail investors may not be fully aware of the long-term effects of rising inflation on their assets and purchasing power. In the context of growing retail participation and significant volatility in crypto-assets and related products, retail investors should be aware of the risks stemming from these. The recent events and subsequent sell-off of crypto assets raises concerns on the appropriate assessment of the risks and the developments of this market segment going forward and requires particular attention of financial institutions and supervisors. Where disclosures are ineffective, these risks are compounded.
- Financial institutions and supervisors should continue to carefully manage environmental related risks and cyber risks. They should ensure that appropriate technologies and adequate control frameworks are in place to address threats to information security and business continuity, including risks stemming from increasingly sophisticated cyber-attacks.
1 MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
The Russian invasion and inflationary pressures have significantly impacted the risk environment of EU securities markets. Recoveries in most equity indices from the beginning of 2022 came to a halt, following the March 2020 market stress, with global equity indices broadly declining (in 1H22: Europe -18%, China -8%, US -20%). This was mostly linked to energy costs and lower trade flows due to the Russian invasion, supply-side bottlenecks linked to the continued effects of the COVID-19 pandemic and the tightening of credit conditions for firms. At the same time, volatility as measured by the European volatility index VSTOXX rose in early March (41%) to about half the levels of March 2020. In Europe, more energy intensive sectors, such as consumer discretionary (-31% YTD), industrials (-29%), and technology (-36%), saw larger price falls than other sectors. Price-earnings ratios tumbled, though they remained above 10-year historical averages (at 3% EU and 9% US respectively). The decreases partly reflect lower earnings expectations for the future, due to the potential long term effects of the pandemic and the impacts of higher long-term interest rates.
Fixed income markets were characterized by investor expectations of slower economic growth, higher
inflation and a less accommodating interest rate environment. Despite a short-lived fall right after the invasion, EU sovereign bond yields rose in 1H22 to levels unseen since 2016 with significant news-flow related volatility (IT +213bps, GR +230bps, DE +150bps). As of end-June, spreads to the Bund also widened, e.g. for Italy (1.9%, +70bps) and Spain (1.1%, +39bps). Corporate bond markets showed sensitivity to the evolving outlook, recording significant selloffs across all rating categories and reduced liquidity. Investment grade (IG) bonds experienced a peak-to-trough fall of 15% (August 2021 to May 2022), nearly twice that of the pandemic, and declined by 12% in the year to June. High-yield (HY) bonds performed slightly worse (‑15%) but their peak-tot rough losses were lower than during the pandemic. Credit spreads widened on concerns that the slowdown could weigh on firms’ debt capacity. Significant spreads upswings were also seen in February with the invasion, and in May and June as rates hikes occurred in the US and were announced for the EA.

The crypto-asset market experienced a continued sell-off in 2Q22 in line with the decline of traditional
financial assets (especially tech equities) with which Bitcoin (BTC) shares a close (40%) correlation. The
collapse of crypto-asset TerraUSD in May and the pausing of customer withdrawals by crypto-asset Celsius in June, added to the shift in investor sentiment away from these assets, sending BTC price to an 18-month low. In May, the largest algorithmic stablecoin (third largest overall), TerraUSD, failed to maintain its peg to the USD after its underlying decentralised finance (DeFi) protocol, Anchor, suffered a confidence run on its deposits. The combination of the sharp fall in crypto-asset prices, and the demise of the Anchor protocol linked to TerraUSD, caused the total value of assets ‘locked’ (deposited) in DeFi smart contracts to fall from over EUR 186bn at the start of May to EUR 62bn by June. In another development in June, centralized finance (CeFi) lending platform, Celsius, halted customer withdrawals of deposits, signaling that it had liquidity issues or a deeper insolvency problem. This coincided with a 21% fall in the Bitcoin price and led Binance to temporarily suspend Bitcoin withdrawals from its exchange. The Celsius token price had fallen by 94% since the start of 2022 with market speculation that it could sell a sizeable stake in crypto asset Ethereum to avoid collapse.
The turmoil triggered by the Russian invasion also affected environmental, social and governance (ESG) markets. In 1Q22, EU ESG equity funds had net outflows of EUR 5bn, compared with average inflows of EUR 11bn per quarter in 2021. ESG bond issuance volumes fell 29% from the start of the year to June, as compared with the same period in 2021. In the banking sector, ESG bond issuance as a share of total bond issuance decreased compared to 2021, though they often enjoy higher subscription levels than non-ESG bonds, allowing banks to pay lower risk premia on new issuances. Despite this, some fundamental factors driving the rise of ESG investing remain in place. Most importantly, investor preferences continue to shift towards sustainable investments, with portfolio allocations increasingly tilted towards ESG investments. Similarly, issuance of ESG bonds by EU corporates remained on par with early 2021, supported by a rapid expansion of the sustainability-linked bond market. This contrasts with a 32% fall in broader EU corporate bond issuance.
2 DEVELOPMENTS IN THE FINANCIAL SECTOR
In 1H22, European investment funds faced heightened volatility in securities markets given the increasingly uncertain economic outlook and the expected increase in interest rates. The performance of most EU fund categories dropped significantly, from a 12-month average monthly performance of 1.6% for equity funds in December 2021 to 0.9% in June 2022. In the meantime, the performance of bond funds turned negative (-0.7%). In contrast, commodity funds outperformed the sector in 1Q22, reflecting the surge in commodity prices following the Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and the sanctions on Russia, before slightly receding, to 2.1%, in end-June. Equity fund flows were also negative (-0.9%). Declining performance led to redemption requests with net outflows in 1H22 totalling 1.6% of the net asset value (NAV) of the fund sector. Bond funds were particularly affected (-4.8% NAV) due to negative performance (-0.7%) and exposures to growing credit and interest risks. Commodity funds experienced outflows (-5.8%), albeit from a low base and only in 2Q22, when their performance declined. MMFs funds also experienced substantial outflows ( -9.2% NAV exceeding the -4.6% NAV observed during COVID-19 stress). MMFs denominated in all currencies experienced outflows, though USD MMFs experienced higher returns (1.1% average monthly performance) than EUR denominated MMFs (-0.1%). While MMFs may generally benefit from a flight-to-quality during uncertain market conditions, investors currently appear to be turning away from fixed-income funds in general. Outflows were partly driven by the expected increase in interest rates. In contrast, real estate funds (1.7% of NAV) and mixed funds (1% of NAV) recorded inflows in 1H22.
The European insurance sector entered 2022 in good shape notwithstanding the adverse developments since the COVID-19 outbreak. During 2021, gross written premiums (GWP) for the life business grew (y-o-y) quite substantially (+14%), while growth was lower for the non-life business (8%). The positive change has partially been driven by the previous reduction in GWP throughout 2020 during the pandemic; although GWP remain still below pre-Covid levels, in particular for life business. The good performance of financial markets and the high returns obtained during 2021 pushed insurer’s profitability up to the levels reached back in 2019, with a median return on assets standing at 0.57% in 4Q21 (0.38% in 4Q20).
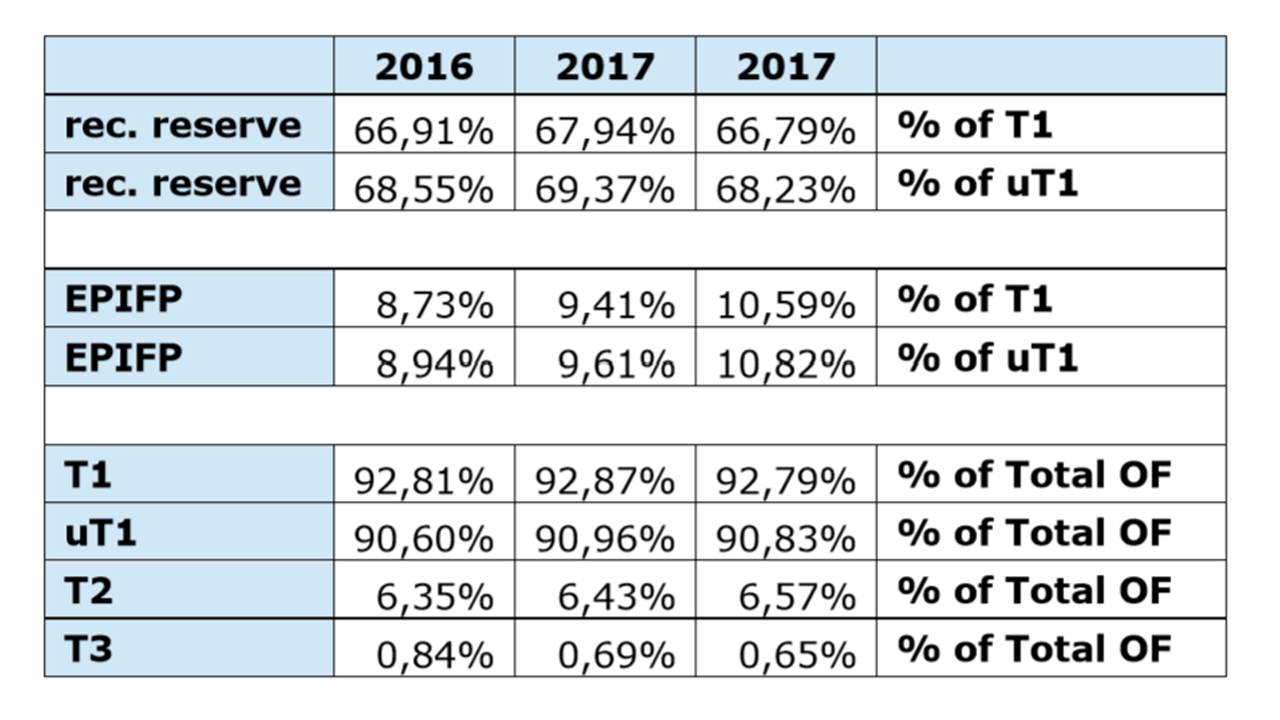
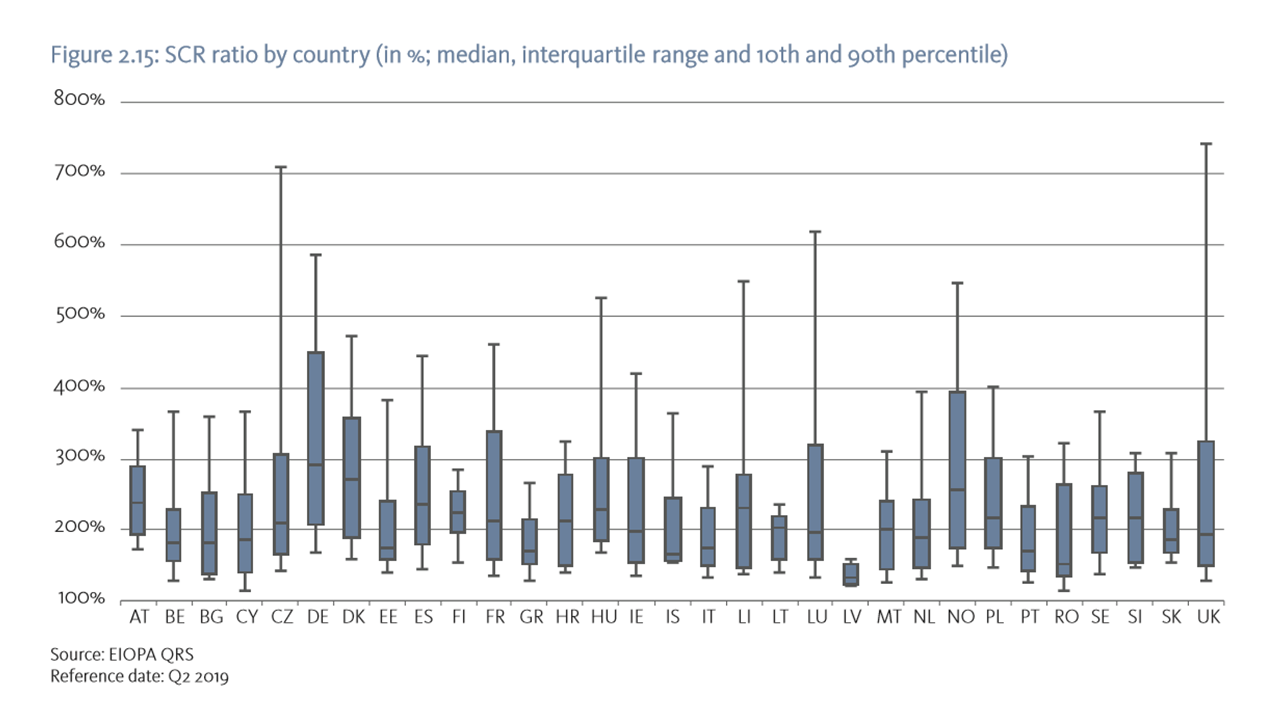
At the beginning of 2022 insurers’ capital buffers on aggregate were solid with a median SCR ratio of 216%. An improvement was observed for life insurers while a slight decline was observed for non-life insurers. As the risk-free interest rate increased throughout 2021, due to the long maturities of life insurers’ liabilities the value of technical provision decreased relatively more than the value of assets, with a positive effect on net capital. This contributed to an increase the median SCR ratio for life insurers, from 216% to 225%. However, the SCR ratio did not reach the high levels observed at the end of 2019 (236%). On the other hand, the median SCR ratio for non-life insurers slightly decreased from 218% towards 211%. This might be driven by the increase in claims negatively affecting the liabilities of some representative undertakings, combined with the fact that asset values declined more than liabilities when interest rates increased given that non-life insurers tend to be characterized by a positive duration gap. Likewise, the financial position of EEA IORPs displayed a recovery in 2021. The total amount of assets grew to EUR 2,713 bn in 4Q21 (From EUR 2,491 bn. in 4Q20), while liabilities remained more or less unchanged. Similarly, the Excess of Assets over Liabilities exhibited a positive trend.
The European banking sector entered 2022 with relatively strong capital- and liquidity positions. The capital ratio (CET1 fully loaded) is, at 15.0% in 1Q22, at the same level as it was before the pandemic broke out (in 4Q19). Yet the capital ratio was 50bps lower than in the previous quarter, mainly driven by rising risk weighted assets (RWA). After a steadily rise in previous quarters, the liquidity coverage ratio (LCR) also slightly deteriorated in 1Q22. A reported LCR ratio of 168.1% in 1Q22 (174.8% in 4Q21) was nevertheless still substantial.
EU banks are facing additional challenges to asset quality and profitability while pandemic-related vulnerabilities continue to loom. Deteriorating economic prospects, high uncertainties and high inflation with a phasing-out of accommodative monetary policy are affecting the outlook for EU banking sector. Loan portfolios with pre-existing vulnerabilities from disruptions caused by the pandemic may also be further affected in a slower economic recovery. Accordingly, 45% banks responding to the EBA’s spring 2022 risk assessment questionnaire (RAQ) indicated their plans to maintain their overlays related to the pandemic to cover potential losses that may materialize in the next quarters, while 35% of banks indicated plan to release them fully or partially. Supervisors should continue to closely monitor the adequacy of banks’ provisions.
The NPL ratio further improved in the first quarter of the year (to 1.9%), mainly driven by decreasing volumes of non-performing loans (NPL). However, rising cost of risks and an increasing share of loans allocated under Stage 2 under IFRS points to slightly deteriorating asset quality. The quality of loans under previous support measures related to the pandemic continues to show signs of deterioration and also requires vigilance. The total volume of loans with expired EBA-compliant moratoria reached EUR 649bn in 1Q22, a 7.8% decline compared to the previous quarter. The volume of subject to public guarantee schemes (PGS) stood at EUR 366bn in 1Q22, almost unchanged compared to the previous quarter. The NPL ratio of loans under expired moratoria and of loans subject to PGS is, at 6.1% and 3.5% in 1Q22, respectively, substantially higher than the overall NPL ratio, and has increased further since 4Q21. PGS loans are mostly concentrated to a few countries only. The allocation of Stage 2 under IRFS 9 for loans under previous support measures is, at 24.5% for loans under expired moratoria and 22.7% for loans subject to PGS, substantially higher than stage 2 allocations for all loans and advances (9.1% in 1Q22). In spite of their slight deterioration in 1Q22, EU banks’ capital and liquidity positions nevertheless provide, for the time being, sufficient cushioning in banks’ balance sheets should the economic situation deteriorate further, or heightened market volatility persist.
Positive operating trends were observed for European banks in 1Q 2022, with a profitability of 6.6% return on equity (ROE) achieved under difficult market conditions, though this is lower than the 7.7% ROE reported in the previous year (1Q21) and lower than the 7.3% ROE of the previous quarter. The contraction can be explained mainly by rising contributions to deposit guarantees schemes and resolutions funds in some countries and various one-off effects, whereas net operating income improved. In 1Q21, lending growth offset a slight decline in net interest margins (NIM) and led to improved net interest income (NII). Net trading income also increased, supported by market volatility. Overall increasing net operating income also outweighed the impact of rising inflation on operating expenses in the first quarter of 2021.
3 IMPACT OF RU-UA WAR ON THE EUROPEAN FINANCIAL SECTORS
Securities markets experienced volatility with some key commodity markets strongly impacted by the Russian invasion and sanctions. Bond yields rose in response to the increasing inflation and anticipated higher rates, while equity markets were volatile and experienced periodic sell-offs. Such volatility can create short-term risks on financial markets. Margin calls on derivatives related to commodities can create liquidity strains for counterparties, as was witnessed by the calls for emergency liquidity assistance for energy traders and the London Metal Exchange suspending nickel trading for five trading days in early March. While commodity derivatives markets in the EU are of limited size relative to EU derivative markets as a whole, these markets create sensitive interlinkages between commodity producing or processing companies, commodity traders, banks acting as intermediaries in the clearing process, central counterparties, and other financial institutions.
The Russian invasion negatively affected credit rating agencies’ (CRA) credit outlook for EEA30 debt. The number of corporate downgrades grew relative to upgrades over 1H22, with a jump in downgrades around the time of the invasion. Russian and Ukrainian ratings were mainly affected, with a series of downgrades in late February and March among both corporates and sovereigns. By mid-April CRAs had withdrawn their Russian ratings in response to the EU measures banning the rating of Russian debt and the provision of rating services to Russian clients. In addition, sanctions have made it difficult for Russia to make sovereign coupon payments. In this context, Russia defaulted on some debt payments due in late June.
Direct impacts of the invasion on investment funds were limited. Exposures to both Russian and Ukrainian counterparties were EUR 50bn (below 0.5% of EU fund assets as of end-January 2022). Some fund exposures were higher, with 300 funds holding over 5% of their portfolios in Russian and Ukrainian assets (total EUR 225bn). The massive fall in prices and liquidity of Russian financial instruments led to serious valuation issues for exposed EU funds. In 1H22, 100 Russia-exposed EU funds (EUR 15bn in combined assets) temporarily suspended redemptions. However, funds with material Russian exposures before the invasion account for a very small share of the EU fund population (less than 0.1% of the EU industry). A number of ETFs tracking Russian benchmarks also suspended share creation. While direct impacts of the Russian invasion on funds, such as losses, were limited, existing risks were amplified by the invasion and the deteriorating macroeconomic outlook. Credit, valuation and liquidity risks remained elevated in the bond fund sector, linked to multiple factors. Bond fund exposures to credit risk stayed elevated, especially for HY funds. The credit quality of the portfolio of HY funds remained close to an average rating between BB- and B+ (5-year low). The likelihood of credit risk materialization also increased with the deteriorating macroeconomic environment and rising interest rates, as visible in the higher credit spreads. In comparison, liquidity risk remained steady for corporate bond funds. Based on asset quality and cash holdings, portfolio liquidity remained stable in 1H22.

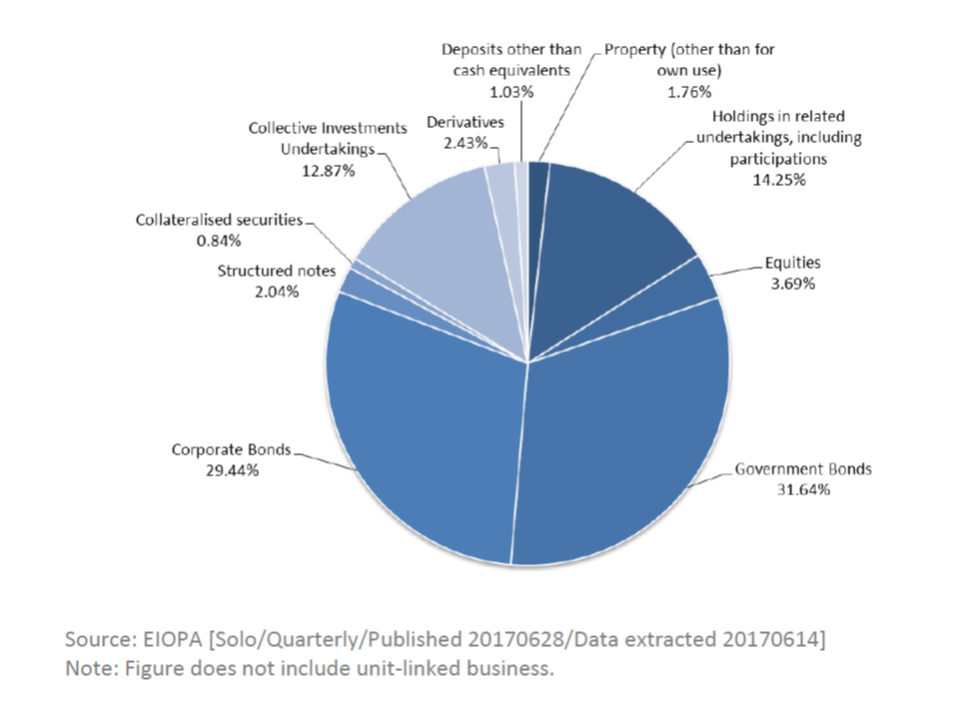
EU insurers’ exposure to assets issued in Russia, Ukraine and Belarus is also limited. These assets amount to EUR 8.3 bn, less than 0.1% of the total investment of the sector. The exposure to Russia is EUR 6.3 bn, which is 0.066% of total investments and the asset exposure to Ukraine is EUR 1.8 bn, 0.019% of total Investments. The exposure to Belarus is negligible. Most of the investments in Russia are through investment funds (84% of total investments). Within funds, the largest asset classes are represented by sovereign bonds and equities associated to unit linked portfolios. A large share of investments to Russia, Ukraine and Belarus (42%) is in index- and unit-linked portfolios, whose risk is born directly by policyholders.
EU insurers have limited activities in the Russian, Ukrainian and Belarusian markets. A small number of EEA groups are active in those countries through subsidiaries. Their size in terms of total assets is minimal if compared to the total assets of the groups. In terms of liability portfolios exposures are also limited. Total technical provision in Russia, Ukraine and Belarus is EUR 0.36 bn., mostly concentrated in the life business.
With regards to IORPs, asset exposures are also limited, at EUR 7.5 bn. (0.23% of total investments). In absolute numbers this is similar to the exposure of the insurance sector. It is worth noting that the size of the IORPs total investment is smaller with respect to the insurance sector.
In the banking sector, direct exposure to Russia and Ukraine appears limited on an EU level and country level. In 1Q22, exposures of the EU/EEA banking sector were at EUR 75.3bn (ca. 0.3% of total assets) towards Russian counterparties, at EUR 10.0bn towards Ukrainian counterparties, and at EUR 2.0bn towards Belorussian counterparties, slightly decreasing towards the three countries compared to the previous quarter. However, exposures are concentrated in a few countries, and a few banks report an up to 10% share of their exposures towards Russia and Ukraine. Some banks also booked substantive provisions related to their exposure to Russia and related to the deteriorating economic environment in the first quarter of this year.
While immediate, first round implications from the Russian invasion appear contained for financial institutions across sectors, the possibility of second round effects is a source of concern. The invasion, heightened uncertainties and inflation are not only weighing on economic prospects, but also affect consumer- and business confidence. Exposures of economic sectors more sensitive to rising energy- and commodity prices require attention across sectors.
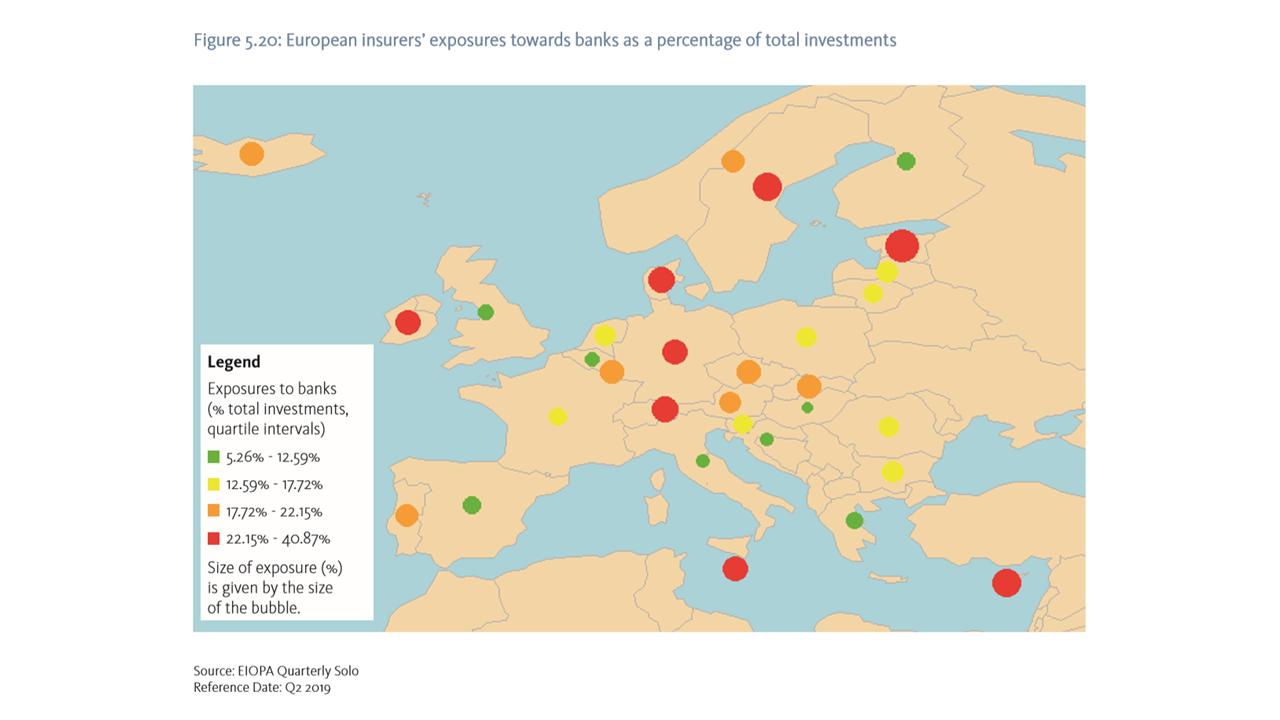
In the insurance sector, second-round effects could emerge via exposures to sectors which, in turn, are highly exposed to the current crisis. Losses in these sectors could have spill-over effects through losses on investments. Two areas could be the most relevant: the exposures of insurers to the banking sector and the exposure to sectors of the economy that are more sensitive to energy and gas prices. Insurers have significant holdings of bank assets, and in this context also hold a significant amount of assets issued by banks that are assumed to be more vulnerable to the evolution of the current crisis. The exposure of EEA insurers to those banks is estimated to only a total amount of EUR 55 bn (0.57% to total investments). Furthermore, insurers have significant asset exposure to sectors sensitive to energy and gas prices.6 The total exposures sum to EUR 174 bn, which includes almost 3% of the equity portfolio of insurers and 7.5% of corporate bond holdings.
In the banking sector, second-round effects could emerge via deteriorating asset quality and further increasing provisioning needs in a deteriorating economic environment. Fee and commission income might also be affected. Banks’ securities portfolios might moreover be negatively affected as fair value declines when interest rates rise. The worsening economic outlook has already resulted in slightly deteriorating early warning indicators for asset quality. The cost of risk increased to 0.51% in 1Q22, a 4bps increase compared to the previous quarter, as borrowers’ debt servicing capacity might be affected by lower economic growth. The increase was mainly driven by the numerator, i.e. by increasing allowances for credit losses. Also, the share of loans allocated under Stage 2 under IFRS increased in 1Q22 and 4Q21, and it another early-warning indicator pointing to slightly deteriorating asset quality. Responses to the EBA RAQ moreover indicate that a majority of banks expect asset quality to deteriorate.
In line with the deteriorating economic outlook and heightened market- and interest rate volatility, bank funding conditions have worsened since the Ukrainian war started and since interest rates increased. Wholesale bank debt spreads have widened for debt and capital instruments across the capital ladder, and particularly for subordinated instruments. Interest rates for bank debt instruments have risen substantially across durations, albeit from extremely low levels. Since the beginning of the war, bank debt issuance activity has been mainly focused on issuing covered bonds, amid challenging market conditions and as banks have begun to roll over expiring long-term central bank funding facilities. Bank funding conditions are likely to stay more challenging while volatility persists and as interest rates continue to rise. Yet current ample liquidity buffers should allow banks to withstand further periods of market turmoil for the time being. In the medium-term, the substitution of expiring extraordinary central bank funding with other sources of funding could prove challenging for some banks.
In spite of positive operating trends in 1Q2022, the outlook for EU bank profitability is subdued. The deteriorating economic environment might affect lending growth and might result in lower loan- and payment-related fee income. Inflationary pressure, higher provisioning needs for expected deteriorating asset quality, costs related to digital transformation and higher compliance costs, e.g. related to the enforcement of sanctions will all likely affect costs, and may offset operating cost savings achieved. While rising rates may have a positive impact on interest income, rising funding costs might also offset additional income from asset repricing.
4 INFLATION AND INTEREST RATE RISKS
The Russian aggression and the sanctions applied contributed to inflation pressures via the resulting supply shocks in energy, food and metals commodities, which added to the supply chain bottlenecks related to the pandemic. Higher energy prices particularly contribute to inflation, widely increasing input and distribution costs. In terms of investment impacts, inflation directly lowers real returns. Inflation changes relative attractiveness of assets both across asset classes and within asset classes. Higher inflation reduces the values of existing assets with fixed returns, such as (most) bonds. By reducing short-term growth, higher rates lower profitability and typically reduce equity values. However, if a rate rise is expected to be effective in increasing long-term growth, it can also increase equity values. Inflation has indirect impacts through its effects on actual and anticipated monetary policy, especially interest rate rises, to reduce demand and bring inflation down. Higher interest rates increase returns on savings and raise borrowing and refinancing costs, reducing debt sustainability. Variable-rate loans face higher debt servicing costs, raising credit risk, including for securitizations backed by variable-rate loans.
In the investment fund sector, interest rate risk increased in a context of rising inflation expectations. Fund portfolios with a longer duration will see their value fall, as inflation drives rates up. However, adjustments are already being made in some funds. Bond fund portfolio durations fell in 1H22, remaining higher for Government (7.6 years, down from 8.6 years) and IG bond funds (6.5 years, down from 7.3 years) than for HY funds (4.3 years, down from 4.8 years). Based on current duration, a 100bps increase of in yield could have a potential impact of -7% on bond fund NAV, about EUR 270bn, which could lead to significant fund outflows. In the MMF sector, funds also significantly reduced the weighted average maturity of their portfolios from 44 days to 30 days (a 3-year low) to lower interest rate risk and improve resilience to a rate rise.
As a period of low inflation and low interest rate is coming to an abrupt end, medium-term risks for asset managers are considerable. Impacts on performance and fund flows are likely to vary across asset classes. For example, the recent US increase in rates led to significant reallocation across fund types from bond funds (-4.7% NAV in 1H22) towards funds offering some form of protection against higher rates. To-date, this contrasts with the EU. In 1H22, US cumulative flows into funds offering protection against higher inflation or rates, such as inflation-protected funds (EUR 1.5bn), loan funds (EUR 13.9bn) and commodity funds (EUR 16.3bn), outpaced their EU equivalents.
Inflation can have a significant impact on borrowers and retail investors. It can heighten vulnerabilities of debtors exposed to flexible lending rates, or where low interest rates on their loans will expire in the near term, including in mortgage lending. Inflation can also have large effects on real returns on savings and investments of retail investors both in the immediate term as well as in the long term. Retail investors may be unaware of inflation or not pay enough attention to its effects on their assets and purchasing power. Consumers can suffer from behavioral biases, such as money illusion or exponential growth bias, that can lead to insufficient saving and investing. Moreover, when inflation is rising, the effects of insufficient saving on long-term wealth become more pronounced.
Insurer positions are affected by inflation on both on the asset and liabilities side typically negative net effects for the non-life segment. On the asset side, insurer investments whose market prices are sensitive to inflation will see a direct or indirect impact through movements of the interest rates. On the liability side, inflation affects insurers through higher costs of claims. This is mostly relevant for non-life lines of business, because non-life guarantees are in nominal terms; crucially, insurers’ build-up provisions for future claims payments and in doing so they must make assumptions today about future price developments. Life insurers are less affected by costs of claims, these typically have liabilities in nominal terms, i.e. claims do not increase with the price development; this is because potential future benefits are often stipulated at inception. Higher general costs can have negative profitability implication for both life and non-life. Finally, the sensitivity on inflation and to interest rate depends also crucially on the duration gap of the undertakings: those with positive duration gaps are more likely to be negatively affected by inflation than those with negative long duration gap, such as life insurers.
On the liability side, the price development relevant for claims expenses, i.e. claims inflation, is particularly important for insurers. Claims inflation tends to outpace the general inflation rate, claims cost depends only to a small extent on inflation as measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP); the reason is that the goods for which insurers pay are significantly different from those which consumers buy. Moreover, claims of insurers encompass various costs, not just costs of goods and services. For Europe, there are no time series available on estimates of future claims inflation; each insurer makes its own business line specific forecast.
Developments in the term structure and risk premia, which remain uncertain, are also having an impact on the net effect on insurer positions, through their exposure to interest rate sensitive assets and the duration of their liabilities. A potential increase in long-term rates would be accompanied by a repricing of the risk premia, and the negative impact on the asset side would not be limited to the fixed income assets but would be reflected to other asset classes through the reduction of market prices. A similar scenario was tested in the EIOPA 2018 Stress Test exercise (Yield Curve Up scenario). This showed relatively high resilience of the insurance sector as a result of the solid capital buffers of the sector in aggregate.
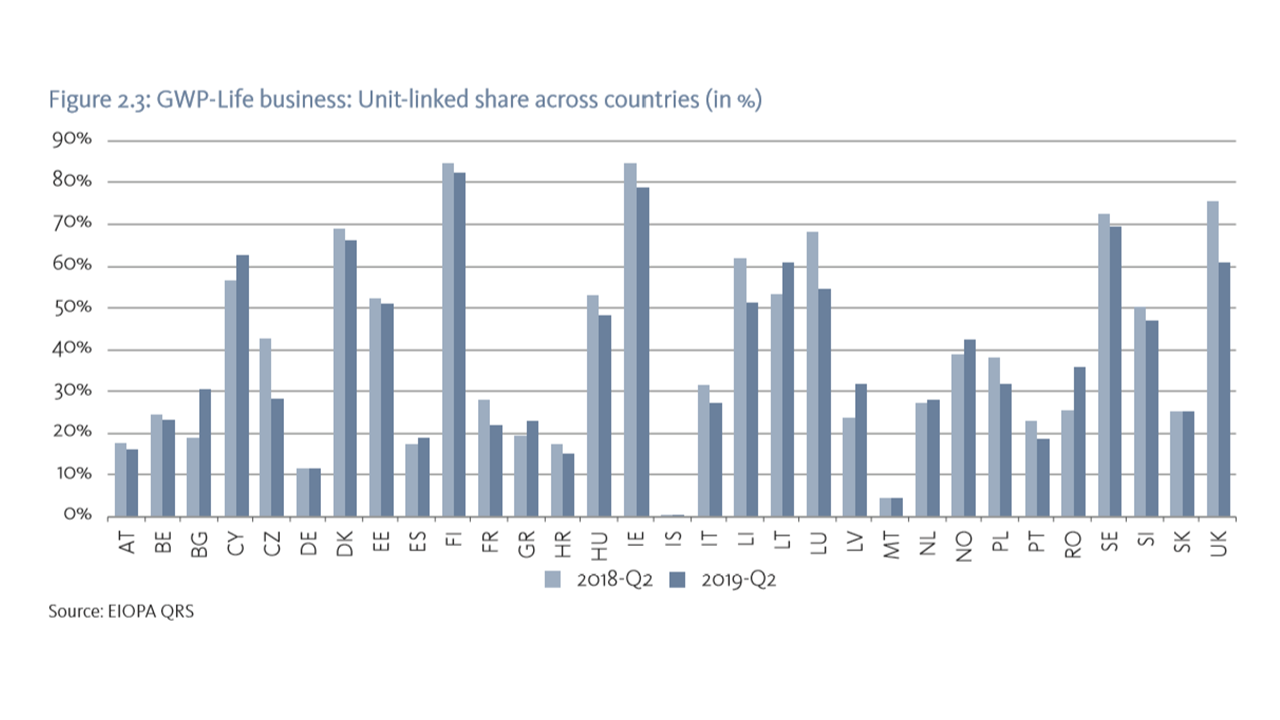
Insurance products can be sensitive to inflation, policyholders and pension beneficiaries face the risk of inflation eroding the real value of their benefits. This ultimately depends on the particular features and details of each contract sold. In the traditional business case of nominal interest rate guarantees, higher inflation than expected (relative to that already factored in the guarantees) has a negative impact in real terms for the policyholder, while contracts with profit sharing may help policyholder returns. In case of unit-linked policies, the policyholder can select the underlying assets from a range of investments e.g. mutual funds. The allocation could involve assets that provide inflation protection or not. Crucially, it requires policyholder financial knowledge/literacy to navigate through the complex dynamics of how investments affect their benefits. In the last years, the share of unit-linked in the life segment continues to increase, now reaching a peak of 39% since the introduction of Solvency II reporting, notwithstanding the considerable differences in the popularity of unit-linked products that remain across countries.
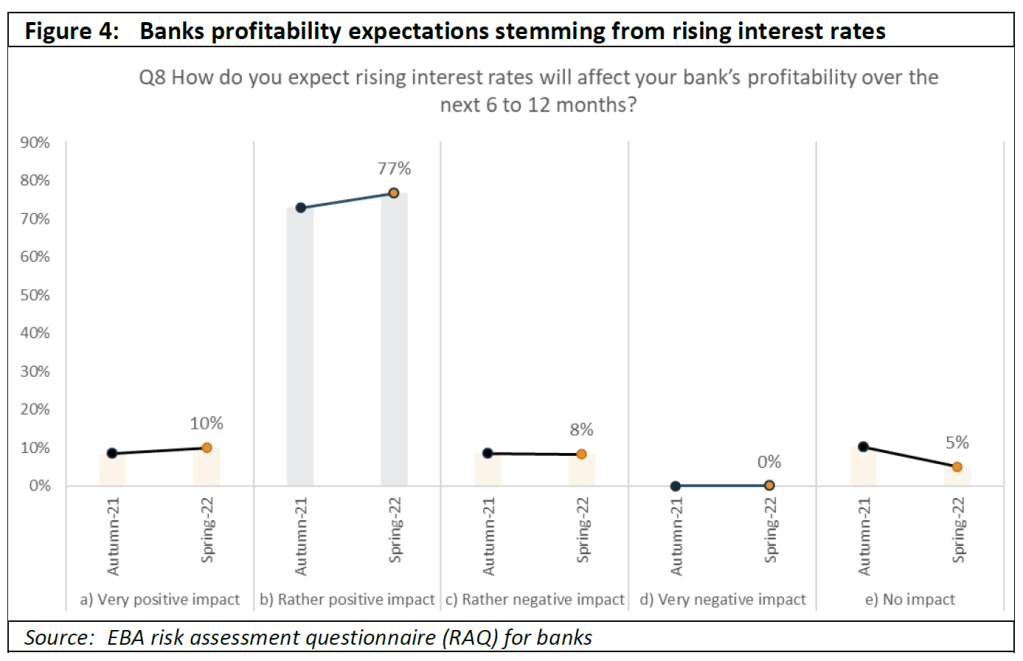
In the banking sector, increasing interest rates are usually expected to have a positive impact on interest income and on net interest margins (NIMs). Accordingly, a vast majority of banks responding to the spring 2022 EBA RAQ expect a positive impact on their profitability from rising interest rates with a repricing of assets. Both banks and analysts are optimistic about the impact of rising rates, and 85% of banks responding to the RAQ expect rising rates to have a positive impact on their profitability. However, analysts also expect an increase in provisions and impairments (at 80%, compared to 15% in the previous RAQ). Since 2014 NIMs have steadily decreased in the very low interest rate environment, and have remained nearly stable since Q1 2021 (1.25% in Q2 2022).
In spite of positive expectations, historic episodes of rising interest rates globally, as well as bank profitability trends in some European countries with an earlier cycle of increasing interest rates offer some indication that NIM may not improve substantially with rising interest rates. Expectations for a substantively positive impact on profitability may be overly optimistic. For example, during periods of stagflation in the USA between 1971 and 1973 and between 1976 and 1980, the sensitivity of NIM to interest rate rises was negligible. Disclosures from banks’ interest rate risks in the banking book (IRRBB) indicate that a parallel shift up of the yield curve positively affects NII for most banks. Yet, while about half of banks disclosing their IRRBB assume that a 200bp parallel rise of the yield curve will add at least a 10% to their NII, a majority of banks assume a negative net impact on their economic value of equity (EVE), a long-term measure of their interest rate risk.
On the liabilities’ side, bank funding costs have increased considerably in line with rising interest rates, which affects profitability. In the next months, analysts expect a broad-based increase in funding costs, including for deposits. Banks, particularly those relying more on wholesale funding, may be affected by a potential substantial increase in funding costs that could even offset positive effects from asset repricing. Banks that need to further build up their loss absorbing capacity could be particularly affected, as a majority of banks consider pricing as main constraint to issuing instruments eligible for MREL. In line with rising inflation, EU banks’ operating costs are also expected to increase further and have already increased substantially in 1Q22.
While general expectations suggest that banks will benefit from a repricing of assets amid rising interest rates, increasing rates might also affect borrower ability to service their debt, and could thus affect asset quality. Coupled with a deteriorating economic outlook, the rising interest rate environment risks in resulting in a reversal of the long-term trend of declining NPL in the banking sector. Rising rates could also contribute to adjustments to the already high real estate valuations in Europe, while the high levels of real estate exposure of EU banks has been identified as a risk. Monetary tightening might also impact lending growth, when, e.g., tightening is accompanied by lower GDP growth, and so could affect interest income.
5 DIGITAL RELATED RISKS
The Russian war in Ukraine and the increasingly volatile geopolitical environment have heightened cybersecurity risks. The frequency of cyber incidents impacting all sectors of activity, as measured by publicly available data, increased significantly in the first quarter of 2022 compared to the same quarter of last year. The potential for escalation involving cyberattacks remains, and a successful attack on a major financial institution or on a critical infrastructure could spread across the entire financial system. Potential consequences also grow ever more far-reaching as the digitalization trend of the financial sector continues. These include disruptions to business continuity, as well as impact on reputation and, in extreme scenarios, liquidity and financial stability. Potential cyberattacks might not be limited to the financial sector only, but also to consumers. In a severe scenario, access to basic services could be impaired, including financial services, and personal data could be compromised.
The sharp market sell-off in May and June 2022 once again demonstrated the extremely volatile and speculative nature of many crypto-assets and related products and the high risks involved for investors, as highlighted in the recent joint-ESAs Warning. The collapse of the Terra ecosystem in May exposed fragilities in stable coins markets, which if left unmanaged, could have ripple effects with negative implications for financial stability, calling for a swift implementation of the Markets in Crypto Assets (MiCA) proposed regulation.
The current geopolitical situation underscores the relevance of the legislation on digital operational resilience (DORA). DORA, which builds on the ESAs Joint Advice in the area of information and communication technology (ICT), is expected to enter into force in early 2023. On 10 May 2022 co-legislators reached a provisional political agreement on its final text. DORA aims to establish a comprehensive framework on digital operational resilience for EU financial entities, and consolidate and upgrade ICT risk requirements spread over various financial services legislation (e.g. PSD2, MiFID, NIS). The geopolitical situation has highlighted some of the risks that DORA will address and underscores the importance of the legislation. The ESAs will be working closely together on the many joint deliverables and new tasks under DORA to help implement the legislation. Moreover, the ESAs, in cooperation with NCAs, have launched a high-level exercise (covering a sample of financial entities) to obtain a better understanding of the exposure of the financial sector to ICT third party providers. The exercise will help authorities and entities to prepare for the forthcoming DORA regime for oversight of critical third-party providers of ICT services.
Digitalization and cyber risks are currently assessed as high and show an increasing trend for the financial sector. In the banking sector, cyber risks are assessed to be very high by both banks and supervisors. The insurance, banking and markets sectors likewise remain on high alert. Since the beginning of the war, cyber-related incidents and disruptions beyond Ukraine and Russia have been rather limited to date, but related risks nevertheless remain unabatedly high. Cyber negative sentiment in the insurance sector, measured as the frequency of negative cyber terms pronounced during insurers’ earning calls, indicates an increased concern in the first quarter of 2022. From an insurance cyber underwriting perspective, cyber-related claims are increasing alongside a growth in the frequency and sophistication of cyber-attacks across financial sectors. In response to increasing cyber-attacks, cyber insurers are strengthening the wording to protect them against losses and could eventually also adjust pricing. Insurers seem to have pushed up attempts to tighten policies and to clarify coverage in the case of a retaliation by Russia and its allies in response to sanctions – the so-called war exclusion, which dictates that losses caused by armed conflict are usually not compensated. In this context, clear communication and disclosure to policyholders on the scope of the coverage and level of protection offered by insurance policies is crucial, in order to avoid a mismatch between their expectations and the actual coverage provided.
Supervisors aim at enhancing monitoring of cyber-related risk framework due to the increased relevance of digitalization and cyber risks. ESMA has recently facilitated increased information-sharing among its competent authorities to ensure supervisors receive timely updates on cyber incidents to inform their work. Turning to the insurance sector, EIOPA has produced exploratory indicators that rely on supervisor responses to the EIOPA Insurance Bottom-Up Survey and on publicly available external data. They will be improved once new supervisory data becomes available. To establish an adequate assessment and mitigation tools to address potential systemic cyber and extreme risks, throughout 2022 and 2023 EIOPA will be working on improving its methodological framework for bottom-up insurance stress tests, including cyber risk.